Helm
This page shows how to use Helm and a pre-built Docker image available at DockerHub in order to operate Hive on MR3 on Kubernetes with multiple nodes. By following the instructions, the user will learn:
- how to start Metastore
- how to run Hive on MR3
After installing Hive on MR3,
change to the directory helm.
cd helm/
In our example, we use Helm 2.16.9.
If install.sh was not executed while installing Hive on MR3,
manually create symbolic links to the two directories kubernetes/conf and kubernetes/key.
mkdir -p ../kubernetes/key
ln -s ../../kubernetes/conf/ hive/conf
ln -s ../../kubernetes/key/ hive/key
Overview
Hive on MR3 consists of four components: Metastore, HiveServer2, MR3 DAGAppMaster, and MR3 ContainerWorkers. The MR3 release can create additional components shown in the following diagram.
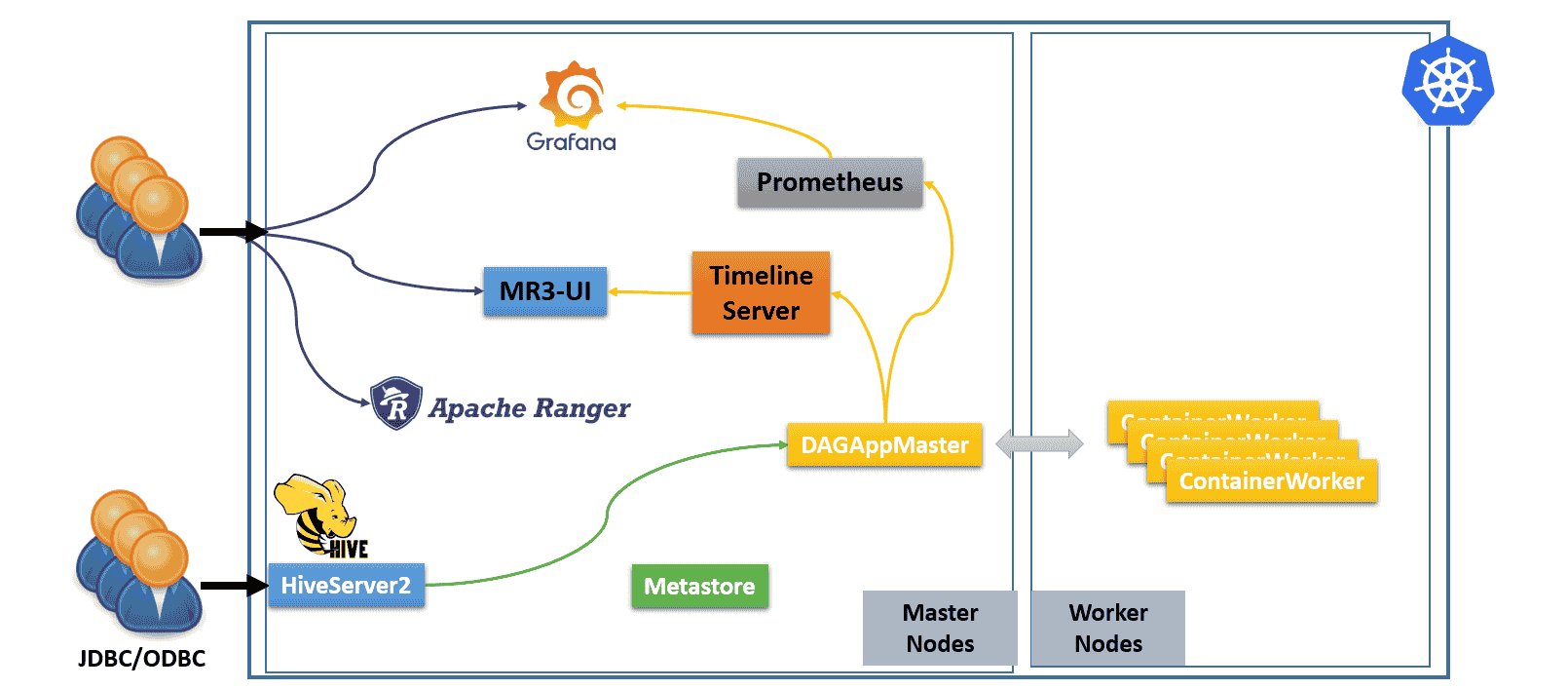
- The user can connect to HiveServer2 (via JDBC/ODBC) which is exposed to the outside of the Kubernetes cluster.
- The user can connect directly to MR3-UI, Grafana, and Ranger.
- Internally we run a Prometheus server to collect metrics from DAGAppMaster.
- A Timeline Server is embedded in DAGAppMaster to collect history logs.
Hive on MR3 requires three types of storage:
- Data source such as HDFS or S3
- Either PersistentVolume or HDFS/S3 for storing transient data
- hostPath volumes for storing intermediate data in ContainerWorker Pods
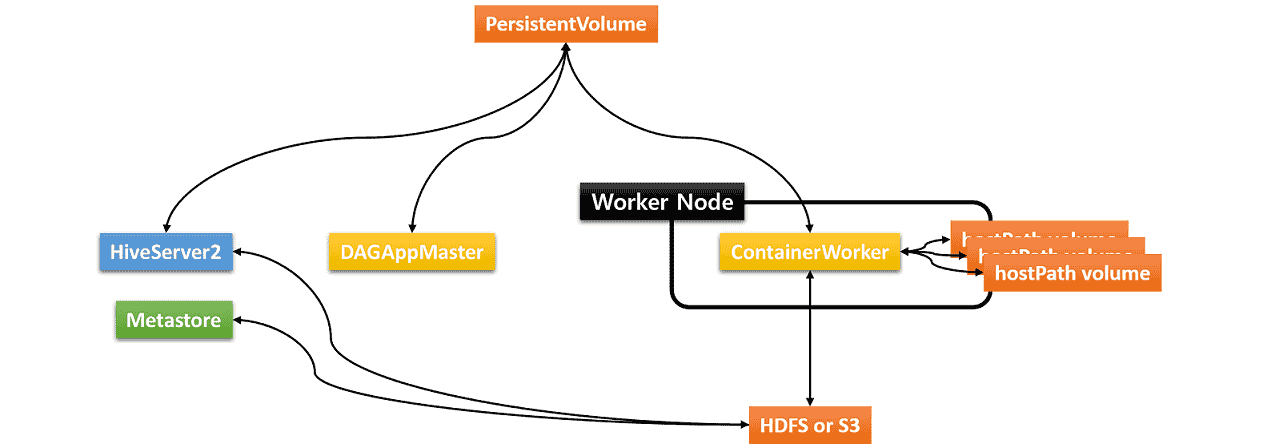
The hostPath volumes are mounted at runtime in each ContainerWorker Pod. These hostPath volumes hold intermediate data to be shuffled between ContainerWorker Pods. In order to be able to mount the same set of hostPath volumes in every ContainerWorker Pod, an identical set of local directories should be ready in all worker nodes (where ContainerWorker Pods are created). For the sake of performance, all the local directories should reside on different local disks.
Running Hive on MR3 involves the following steps.
- The user creates
values-hive.yamlto configure Pods. - The user updates
hive-site.xml,mr3-site.xml, andtez-site.xmlin the configuration directoryhive/conf. - The user installs Helm chart for Hive on MR3 with
values-hive.yamlto start Metastore and HiveServer2. A DAGAppMaster Pod is created by HiveServer2, and ContainerWorker Pods are created by DAGAppMaster.
In the second step,
updating hive-site.xml and mr3-site.xml is usually enough to get started
as the default values in tez-site.xml work well in common settings.
Configuring for Metastore
Create a new file hive/values-hive.yaml
and update the following fields
to override the default values in hive/values.yaml.
vi hive/values-hive.yaml
create:
metastore: true
metastore:
databaseHost: 192.168.10.1 # use your IP address (where the MySQL database is running)
databaseName: hivemr3
dbType: mysql
warehouseDir: s3a://hivemr3/warehouse
- Set
create.metastoreto true because we will create a Metastore Pod. - Set
metastore.databaseHostto the IP address of the MySQL server for Metastore. In our example, the MySQL server is running at the IP address192.168.10.1. - Set
metastore.databaseNameto the database name for Metastore in the MySQL server. - Set
metastore.dbTypeto the database type for Metastore which is used as an argument toschematool(mysqlfor MYSQL,postgresfor PostgreSQL,mssqlfor MS SQL). - Set
metastore.warehouseDirto the HDFS directory or the S3 bucket storing the warehouse (e.g.,hdfs://hdfs.server:8020/hive/warehouseors3a://hivemr3/hive/warehouse). Note that for using S3, we should use prefixs3a, nots3.
Docker image
We use a pre-built Docker image available at DockerHub.
Open hive/values-hive.yaml
set update the following fields.
- Set
docker.imageto the Docker image for all Pods except for ContainerWorker Pods. - Set
docker.containerWorkerImageto the Docker image for ContainerWorker Pods.
vi hive/values-hive.yaml
docker:
image: mr3project/hive:4.0.0.mr3.2.4
containerWorkerImage: mr3project/hive:4.0.0.mr3.2.4
Resources for Metastore and HiveServer2 Pods
Open hive/values-hive.yaml
and set the resources for HiveServer2 and Metastore Pods.
heapSize specifies the memory size (in MB) for the Java process
and should be set to a value equivalent to resources.requests.memory.
vi hive/values-hive.yaml
metastore:
resources:
requests:
cpu: 4
memory: 16Gi
limits:
cpu: 4
memory: 16Gi
heapSize: 16384
hive:
resources:
requests:
cpu: 4
memory: 16Gi
limits:
cpu: 4
memory: 16Gi
heapSize: 16384
Resources for DAGAppMaster Pod
By default, we allocate 16GB of memory and 4 CPUs to a DAGAppMaster Pod.
To adjust resources, update hive/conf/mr3-site.xml.
vi hive/conf/mr3-site.xml
<property>
<name>mr3.am.resource.memory.mb</name>
<value>16384</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>mr3.am.resource.cpu.cores</name>
<value>4</value>
</property>
Setting host aliases (optional)
To use host names (instead of IP addresses) when configuring Hive on MR3, the user should update:
hostAliasesfield inhive/values-hive.yaml- configuration key
mr3.k8s.host.aliasesinhive/conf/mr3-site.xml
For example,
if metastore/databaseHost or metastore/warehouseDir in values-hive.yaml
uses a host name called orange0/orange1 with IP address 192.168.10.100/192.168.10.1,
update as follows.
vi hive/values-hive.yaml
hostAliases:
- ip: "192.168.10.100"
hostnames:
- "orange0"
- ip: "192.168.10.1"
hostnames:
- "orange1"
vi hive/conf/mr3-site.xml
<property>
<name>mr3.k8s.host.aliases</name>
<value>orange0=192.168.10.100,orange1=192.168.10.1</value>
</property>
Configuring storage for transient data
The user can use either a PersistentVolume or HDFS/S3 to store transient data (e.g., results of running queries to be passed from ContainerWorkers to HiveServer2). To use a PersistentVolume, follow the instruction in 1. Creating and mounting PersistentVolume. To use HDFS/S3, follow the instruction in 2. Using HDFS/S3.
1. Creating and mounting PersistentVolume
The workDir fields in hive/values-hive.yaml
specify how to create a PersistentVolume and a corresponding PersistentVolumeClaim.
- The field
workDir.createspecifies whether or not to create PersistentVolume and PersistentVolumeClaim. - The field
workDir.usespecifies whether or not use PersistentVolumeClaim.
Set workDir.create to false (but workDir.use to true)
if a PersistentVolume and a corresponding PersistentVolumeClaim have already been created (e.g., on Amazon EKS).
In our example, we use an NFS volume by setting workDir.isNfs to true.
The NFS server runs at 192.168.10.1, uses a directory /home/nfs/hivemr3,
and allows up to 100GB of disk space.
We also specify the size of the storage to be used by Hive on MR3 in workDir.volumeClaimSize.
The PersistentVolume should be writable to the user with UID 1000.
vi hive/values-hive.yaml
workDir:
create: true
use: true
isNfs: true
nfs:
server: "192.168.10.1"
path: "/home/nfs/hivemr3"
volumeSize: 100Gi
volumeClaimSize: 10Gi
In order to use different types of PersistentVolumes,
the user should set the field workDir.isNfs to false
and set the field workDir.volumeStr appropriately
to a string to be used in hive/templates/workdir-pv.yaml.
2. Using HDFS/S3
As we do not use a PersistentVolume,
set both fields workDir.create and workDir.use to false in hive/values-hive.yaml.
vi hive/values-hive.yaml
workDir:
create: false
use: false
Set the configuration keys hive.exec.scratchdir and hive.query.results.cache.directory in hive/conf/hive-site.xml to point to the directory on HDFS or S3 for storing transient data.
- The directory on HDFS must be writable to the user running HiveServer2 and have directory permission 733. If it does not exist, HiveServer2 automatically creates a new directory with permission 733.
- To use S3, we should use prefix
s3a, nots3. The configuration keymr3.am.staging.dir.check.ownership.permissionshould be set to false inhive/conf/mr3-site.xmlbecause S3 is an object store which only simulates directories without maintaining ownership and permission.
vi hive/conf/hive-site.xml
<property>
<name>hive.exec.scratchdir</name>
<value>s3a://hivemr3/workdir</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.query.results.cache.directory</name>
<value>s3a://hivemr3/workdir/_resultscache_</value>
</property>
- Update
hive.repl.rootdironly if the user plans to execute theREPL DUMPcommand. - Do not update
hive.downloaded.resources.dirbecause it should point to a directory on the local file system.
Configuring S3 (optional)
To access S3 storage,
additional configuration keys should be set in hive/conf/core-site.xml.
Open hive/conf/core-site.xml and set configuration keys for S3.
The configuration key fs.s3a.endpoint should be set to point to the storage server.
vi hive/conf/core-site.xml
<property>
<name>fs.s3a.aws.credentials.provider</name>
<value>com.amazonaws.auth.EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>fs.s3a.endpoint</name>
<value>http://orange0:9000</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>fs.s3a.path.style.access</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
When using
the class EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider to read AWS credentials,
add two environment variables AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY in hive/env-secret.sh.
Since hive/env-secret.sh is mounted as a Secret inside Metastore and HiveServer2 Pods,
it is safe to write AWS access key ID and secret access key in hive/env-secret.sh.
vi hive/env-secret.sh
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=_your_aws_access_key_id_
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=_your_aws_secret_secret_key_
Note that AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY are already appended
to the values of the configuration keys mr3.am.launch.env and mr3.container.launch.env in hive/conf/mr3-site.xml.
For the security purpose, the user should NOT write AWS access key ID and secret access key in hive/conf/mr3-site.xml.
vi hive/conf/mr3-site.xml
<property>
<name>mr3.am.launch.env</name>
<value>LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/opt/mr3-run/hadoop/apache-hadoop/lib/native,HADOOP_CREDSTORE_PASSWORD,AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY,AWS_REGION</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>mr3.container.launch.env</name>
<value>LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/opt/mr3-run/hadoop/apache-hadoop/lib/native,HADOOP_CREDSTORE_PASSWORD,AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY,AWS_REGION</value>
</property>
Configuring Metastore Pod
Update hive/templates/metastore.yaml to remove nodeAffinity as we do not use node affinity rules.
vi hive/templates/metastore.yaml
affinity:
# nodeAffinity:
# requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
# nodeSelectorTerms:
# - matchExpressions:
# - key: roles
# operator: In
# values:
# - "masters"
By default, Metastore does not initialize schema.
If it is the first time to run Metastore and the user needs to initialize schema,
open hive/values-hive.yaml
and set metastore.initSchema set to true.
vi hive/values-hive.yaml
metastore:
initSchema: true
Configuring HiveServer2 Pod
(no further change to hive/templates/hive.yaml)
Configuring Service for HiveServer2
The manifest hive/templates/hiveserver2-service.yaml
defines a Service for exposing HiveServer2 to the outside of the Kubernetes cluster.
The user should specify a public IP address for HiveServer2
so that clients can connect to it from the outside of the Kubernetes cluster.
By default, HiveServer2 uses port 9852 for Thrift transport and port 10001 for HTTP transport.
In our example, we expose HiveServer2 at 192.168.10.1.
In hive/values-hive.yaml,
set hive.externalIp to the public IP address of HiveServer2.
vi hive/values-hive.yaml
hive:
externalIp: 192.168.10.1 # use your IP address
For secure communication using SSL, a valid host name for the public IP address is required.
Configuring MR3 DAGAppMaster and ContainerWorker Pods
As a prerequisite,
every worker node where ContainerWorker Pods may run
should have an identical set of local directories for storing intermediate data.
These directories are mapped to hostPath volumes in each ContainerWorker Pod.
Set the configuration key mr3.k8s.pod.worker.hostpaths to the list of local directories in hive/conf/mr3-site.xml.
vi hive/conf/mr3-site.xml
<property>
<name>mr3.k8s.pod.worker.hostpaths</name>
<value>/data1/k8s,/data2/k8s,/data3/k8s</value>
</property>
Configuring security
Update the following configuration keys in hive/conf/hive-site.xml.
- The two configuration keys
javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserNameandjavax.jdo.option.ConnectionPasswordshould match the user name and password of the MySQL server for Metastore. hive.metastore.pre.event.listenersis set to empty because we do not enable security on the Metastore side.
vi hive/conf/hive-site.xml
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName</name>
<value>root</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword</name>
<value>passwd</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.pre.event.listeners</name>
<value></value>
</property>
Check the configuration for authentication and authorization:
vi hive/conf/hive-site.xml
<property>
<name>hive.security.authenticator.manager</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.security.HadoopDefaultAuthenticator</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.authorization.manager</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.security.authorization.plugin.sqlstd.SQLStdConfOnlyAuthorizerFactory</value>
</property>
Configuring resources
In hive/conf/hive-site.xml, the following configuration keys specify
the resource to be allocated to a Map Task, a Reduce Task, or a ContainerWorker.
In our example, we allocate 4GB of memory and a single core to a Map Task and a Reduce Task,
and 16GB of memory and four cores to a ContainerWorker.
vi hive/conf/hive-site.xml
<property>
<name>hive.mr3.map.task.memory.mb</name>
<value>4096</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mr3.map.task.vcores</name>
<value>1</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mr3.reduce.task.memory.mb</name>
<value>4096</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mr3.reduce.task.vcores</name>
<value>1</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mr3.all-in-one.containergroup.memory.mb</name>
<value>16384</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mr3.all-in-one.containergroup.vcores</name>
<value>4</value>
</property>
When updating these configuration keys, we should meet the following requirements:
hive.mr3.map.task.memory.mb≤hive.mr3.all-in-one.containergroup.memory.mbhive.mr3.map.task.vcores≤hive.mr3.all-in-one.containergroup.vcoreshive.mr3.reduce.task.memory.mb≤hive.mr3.all-in-one.containergroup.memory.mbhive.mr3.reduce.task.vcores≤hive.mr3.all-in-one.containergroup.vcores
Starting Hive on MR3
hive/values-hive.yaml should not contain two separate sections for the same key.
In the following example,
the field metastore.databaseHost is ignored because of the second section for the key metastore.
metastore:
databaseHost: 192.168.10.1
metastore:
initSchema: true
Before starting Hive on MR3,
make sure that no ConfigMaps and Services exist in the namespace hivemr3.
For example, the user may see ConfigMaps and Services left over from a previous run.
kubectl get configmaps -n hivemr3
NAME DATA AGE
mr3conf-configmap-master 1 16m
mr3conf-configmap-worker 1 16m
kubectl get svc -n hivemr3
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service-master-1237-0 ClusterIP 10.105.238.21 <none> 80/TCP 11m
service-worker ClusterIP None <none> <none> 11m
In such a case, manually delete these ConfigMaps and Services.
kubectl delete configmap -n hivemr3 mr3conf-configmap-master mr3conf-configmap-worker
kubectl delete svc -n hivemr3 service-master-1237-0 service-worker
Install Helm chart for Hive on MR3 with hive/values-hive.yaml.
We use hivemr3 for the namespace.
Metastore automatically downloads a MySQL connector
from https://cdn.mysql.com/Downloads/Connector-J/mysql-connector-java-8.0.28.tar.gz.
helm install --namespace hivemr3 hive -f hive/values-hive.yaml
2025/03/22 00:58:22 found symbolic link in path: /home/gitlab-runner/mr3-prep/helm/hive/conf resolves to /home/gitlab-runner/mr3-prep/kubernetes/conf
2025/03/22 00:58:22 found symbolic link in path: /home/gitlab-runner/mr3-prep/helm/hive/key resolves to /home/gitlab-runner/mr3-prep/kubernetes/key
NAME: braided-kangaroo
LAST DEPLOYED: Sat Mar 22 00:58:22 2025
NAMESPACE: hivemr3
STATUS: DEPLOYED
...
==> v1/ConfigMap
NAME DATA AGE
client-am-config 4 1s
env-configmap 1 1s
hivemr3-conf-configmap 18 1s
...
Check if all ConfigMaps are non-empty.
If the DATA column for hivemr3-conf-configmap is 0,
try to remove unnecessary files in the configuration directory conf.
This usually happens when a temporary file (e.g., .hive-site.xml.swp) is kept at the time of installing Helm chart.
Helm mounts the following files inside the Metastore and HiveServer2 Pods:
hive/env.shhive/conf/*
In this way, the user can completely specify the behavior of Metastore and HiveServer2 as well as DAGAppMaster and ContainerWorkers.
In order to make any changes to these files effective,
the user should restart Metastore and HiveServer2
after deleting existing ConfigMaps and Services in the namespace hivemr3.
Find three Pods running in the Minikube cluster: Metastore, HiveServer2, and MR3 DAGAppMaster. HiveServer2 Pod becomes ready after a readiness probe contacts it. Depending on the configuration for readiness probe, HiveServer2 may restart once before running normally. No ContainerWorkers Pods are created until queries are submitted.
kubectl get pods -n hivemr3
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hivemr3-hiveserver2-54bfbd664d-lznkd 1/1 Running 0 76s
hivemr3-metastore-0 1/1 Running 0 76s
mr3master-2989-0-7cc767554d-vzw7f 1/1 Running 0 60s
The user can check the log of the DAGAppMaster Pod to make sure that it has started properly.
kubectl logs -f -n hivemr3 mr3master-2989-0-7cc767554d-vzw7f
...
2025-03-21T15:59:59,465 INFO [DAGAppMaster-1-14] DAGTimeoutHandler$: DAG timeout check: 0 DAGs
2025-03-21T15:59:59,542 INFO [K8sContainerLauncher-2-1] K8sContainerLauncher: Resynchronizing Pod states for appattempt_1872989_0000_000000: 0
After starting Metastore,
the user should set initSchema to false
so as not to inadvertently initialize schema again.
vi hive/values-hive.yaml
metastore:
initSchema: false
Running Beeline
The user may use any client program (not necessarily Beeline included in the MR3 release) to connect to HiveServer2
via the Service created with yaml/hiveserver2-service.yaml
(which opens a Thrift port 9852 and an HTTP port 10001 by default).
In our example, we run Beeline inside the Hiveserver2 Pod.
kubectl exec -n hivemr3 -it hivemr3-hiveserver2-54bfbd664d-lznkd -- /bin/bash -c 'export PS1="$ "; exec /bin/bash'
export USER=root
/opt/mr3-run/hive/run-beeline.sh
...
Connecting to jdbc:hive2://hivemr3-hiveserver2-54bfbd664d-lznkd:9852/;;;
Connected to: Apache Hive (version 4.0.0)
Driver: Hive JDBC (version 4.0.0)
Transaction isolation: TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ
Beeline version 4.0.0 by Apache Hive
0: jdbc:hive2://hivemr3-hiveserver2-54bfbd664>
After executing a few queries, ContainerWorker Pods are created.
kubectl get pods -n hivemr3
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hivemr3-hiveserver2-54bfbd664d-lznkd 1/1 Running 0 3m30s
hivemr3-metastore-0 1/1 Running 0 3m30s
mr3master-2989-0-7cc767554d-vzw7f 1/1 Running 0 3m14s
mr3worker-6fb6-1 1/1 Running 0 17s
mr3worker-6fb6-2 1/1 Running 0 17s
mr3worker-6fb6-3 1/1 Running 0 17s
Stopping Hive on MR3
In order to terminate Hive on MR3, the user should first delete the DAGAppMaster Pod and then delete Helm chart, not the other way. This is because deleting Helm chart revokes the ServiceAccount object which DAGAppMaster uses to delete ContainerWorker Pods. Hence, if the user deletes Helm chart first, all remaining Pods should be deleted manually.
Delete Deployment for DAGAppMaster which in turn deletes all ContainerWorker Pods automatically.
kubectl get deployment -n hivemr3
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
hivemr3-hiveserver2 1/1 1 1 3m55s
mr3master-2989-0 1/1 1 1 3m39s
kubectl -n hivemr3 delete deployment mr3master-2989-0
deployment.apps "mr3master-2989-0" deleted
Delete Helm chart.
helm delete braided-kangaroo
release "braided-kangaroo" deleted
As the last step, the user will find that the following objects belonging to the namespace hivemr3 are still alive:
- two ConfigMaps
mr3conf-configmap-masterandmr3conf-configmap-worker - Service for DAGAppMaster, e.g.,
service-master-1627-0 - Service
service-worker
kubectl get configmaps -n hivemr3
NAME DATA AGE
mr3conf-configmap-master 1 4m38s
mr3conf-configmap-worker 1 4m32s
kubectl get svc -n hivemr3
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service-master-2989-0 ClusterIP 10.96.74.65 <none> 80/TCP,9890/TCP 4m48s
service-worker ClusterIP None <none> <none> 4m45s
These ConfigMaps and Services are not deleted by the command helm delete because
they are created not by Helm but by HiveServer2 and DAGAppMaster.
Hence the user should delete these ConfigMaps and Services manually.
kubectl delete configmap -n hivemr3 mr3conf-configmap-master mr3conf-configmap-worker
configmap "mr3conf-configmap-master" deleted
configmap "mr3conf-configmap-worker" deleted
kubectl delete svc -n hivemr3 service-master-2989-0 service-worker
service "service-master-2989-0" deleted
service "service-worker" deleted