With Ranger
This page explains additional steps for using Ranger for authorization in Hive on MR3. Using Ranger for authorization has the following prerequisite:
- A database server for Ranger is running. It may be the same database server for Metastore. In our example, we assume a MySQL database.
To run Ranger, we need to check or update the following files.
├── yaml
│ ├── ranger-service.yaml
│ └── ranger.yaml
├── conf
│ ├── hive-site.xml
│ ├── ranger-hive-audit.xml
│ └── ranger-hive-security.xml
├── ranger-key
│ ├── install.properties
│ └── solr.in.sh
└── ranger-conf
├── core-site.xml
├── solr-security.json
└── ranger-admin-site.xml.append
yaml/ranger-service.yaml
This manifest defines a Service for exposing Ranger to the outside of the Kubernetes cluster. The user should specify an IP address with a valid host name.
vi yaml/ranger-service.yaml
spec:
externalIPs:
- 192.168.10.1
yaml/ranger.yaml
vi yaml/ranger.yaml
spec:
template:
spec:
hostAliases:
- ip: "192.168.10.100"
hostnames:
- "orange0"
- ip: "192.168.10.1"
hostnames:
- "orange1"
nodeSelector:
roles: masters
containers:
- image: mr3project/ranger:2.6.0
name: solr
- image: mr3project/ranger:2.6.0
name: ranger
- The
spec.hostAliasesfield lists aliases for hosts that may not be found in the default DNS. Usually it suffices to include three hosts:
- the host running MySQL for Ranger outside the Kubernetes cluster;
- the host running HiveServer2 inside the Kubernetes cluster;
- the host running Ranger inside the Kubernetes cluster.
In our example,
orange0is the host running MySQL for Ranger andorange1is the host name assigned to HiveServer2 and Ranger.
- The
nodeSelectorfield is optional and can be set to specify how to place a Ranger Pod. - The
imagefield in thespec.containerssection specifies the Docker image for Ranger. We use the pre-built Docker imagemr3project/ranger:2.6.0.
PersistentVolumeClaim
Ranger uses the PersistentVolumeClaim workdir-pvc created for Hive on MR3.
The PersistentVolume should be writable to user nobody (corresponding to root user).
To use a local directory inside the Docker container instead (e.g., if PersistentVolumeClaim is not created for Hive on MR3), comment out the following lines.
vi yaml/ranger.yaml
# - name: work-dir-volume
# mountPath: /opt/mr3-run/ranger/work-dir/
# - name: work-dir-volume
# persistentVolumeClaim:
# claimName: workdir-pvc
conf/hive-site.xml
The following configuration keys should be set to use Ranger for authorization in HiveServer2.
vi conf/hive-site.xml
<property>
<name>hive.security.authenticator.manager</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.security.SessionStateUserAuthenticator</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.authorization.manager</name>
<value>org.apache.ranger.authorization.hive.authorizer.RangerHiveAuthorizerFactory</value>
</property>
conf/ranger-hive-audit.xml
The configuration key xasecure.audit.destination.solr.urls should use the host name assigned to Ranger.
vi conf/ranger-hive-audit.xml
<property>
<name>xasecure.audit.destination.solr.urls</name>
<value>http://orange1:6083/solr/ranger_audits</value>
</property>
conf/ranger-hive-security.xml
The configuration key ranger.plugin.hive.service.name should use the Ranger service for HiveServer2.
The configuration key ranger.plugin.hive.policy.rest.url should use the host name assigned to Ranger.
vi conf/ranger-hive-security.xml
<property>
<name>ranger.plugin.hive.service.name</name>
<value>ORANGE_hive</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>ranger.plugin.hive.policy.rest.url</name>
<value>http://orange1:6080</value>
</property>
ranger-key/install.properties
vi ranger-key/install.properties
DB_FLAVOR=MYSQL
SQL_CONNECTOR_JAR=/opt/mr3-run/lib/mysql-connector-java-8.0.28.jar
db_root_user=root
db_root_password=passwd
db_host=192.168.10.100
db_password=password
rangerAdmin_password=rangeradmin1
audit_solr_urls=http://orange1:6083/solr/ranger_audits
audit_solr_user=
audit_solr_password=
policymgr_external_url=http://orange1:6080
policymgr_http_enabled=true
DB_FLAVORandSQL_CONNECTOR_JARshould match the database connector jar file.db_root_useranddb_root_passwordshould be set to the ID and password of the root user of MySQL for Ranger.db_hostshould be set to the IP address or the host name of the MySQL database for Ranger.db_passwordspecifies a password for the userrangeradminwhich is use only internally by Ranger.rangerAdmin_passwordspecifies the initial password for the useradminon the Ranger Admin UI.audit_solr_urlsspecifies the address for the configuration keyranger.audit.solr.urls.- Set to empty or remove two variables
audit_solr_userandaudit_solr_passwordrelated to authentication for auditing. policymgr_external_urlshould be set to the Ranger admin URL.policymgr_http_enabledshould be set to true.
When using a MySQL server,
Ranger automatically downloads a MySQL connector
from https://cdn.mysql.com/Downloads/Connector-J/mysql-connector-java-8.0.28.tar.gz.
The user should check the compatibility between the server and the connector.
For example,
a MySQL server created with a Docker image 5.7.37-0ubuntu0.18.04.1
is not fully compatible.
ranger-key/solr.in.sh
vi ranger-key/solr.in.sh
SOLR_SSL_ENABLED=false
SOLR_AUTH_TYPE="basic"
SOLR_AUTHENTICATION_OPTS="-Dbasicauth=solr:solrRocks"
- Set
SOLR_SSL_ENABLEDto false because we do not use SSL for Solr. - Set
SOLR_AUTH_TYPEandSOLR_AUTHENTICATION_OPTSas shown above because we do not use Kerberos for Solr.
ranger-conf/core-site.xml
Set the configuration key hadoop.security.authentication to simple to disable Kerberos authentication.
vi ranger-conf/core-site.xml
<property>
<name>hadoop.security.authentication</name>
<value>simple</value>
</property>
ranger-conf/solr-security.json
Set the configuration for authentication and authorization in Solr as follows.
vi ranger-conf/solr-security.json
{
"authentication": {
"blockUnknown": false,
"class": "solr.BasicAuthPlugin",
"credentials":{
"solr":"IV0EHq1OnNrj6gvRCwvFwTrZ1+z1oBbnQdiVC3otuq0= Ndd7LKvVBAaZIF0QAVi1ekCfAJXr1GGfLtRUXhgrF8c="
}
},
"authorization": {
"class": "solr.RuleBasedAuthorizationPlugin"
}
}
ranger-conf/ranger-admin-site.xml.append
If Kerberos is not used, clear the contents except the last line.
vi ranger-conf/ranger-admin-site.xml.append
</configuration>
Running Ranger
In order to run Ranger, the user can execute the script run-ranger.sh
(before executing Metastore and HiveServer2).
./run-ranger.sh
namespace/hivemr3 created
configmap/hivemr3-ranger-conf-configmap created
secret/hivemr3-ranger-secret created
deployment.apps/hivemr3-ranger created
service/ranger created
kubectl get pods -n hivemr3
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hivemr3-ranger-0 2/2 Running 0 102s
./run-metastore.sh
./run-hive.sh
Creating a Ranger service
After running Ranger, the user can check if Ranger has started properly.
kubectl logs -n hivemr3 hivemr3-ranger-0 -c ranger
...
Installation of Ranger PolicyManager Web Application is completed.
Starting Apache Ranger Admin Service
Apache Ranger Admin Service with pid 1696 has started.
Before executing queries,
the user should create a new Ranger service ORANGE_hive
(if it is not available yet).
The user can access Ranger Admin UI at http://orange1:6080
(specified by policymgr_external_url in ranger-key/install.properties).
Login to Ranger Admin UI with user admin and password rangeradmin1.
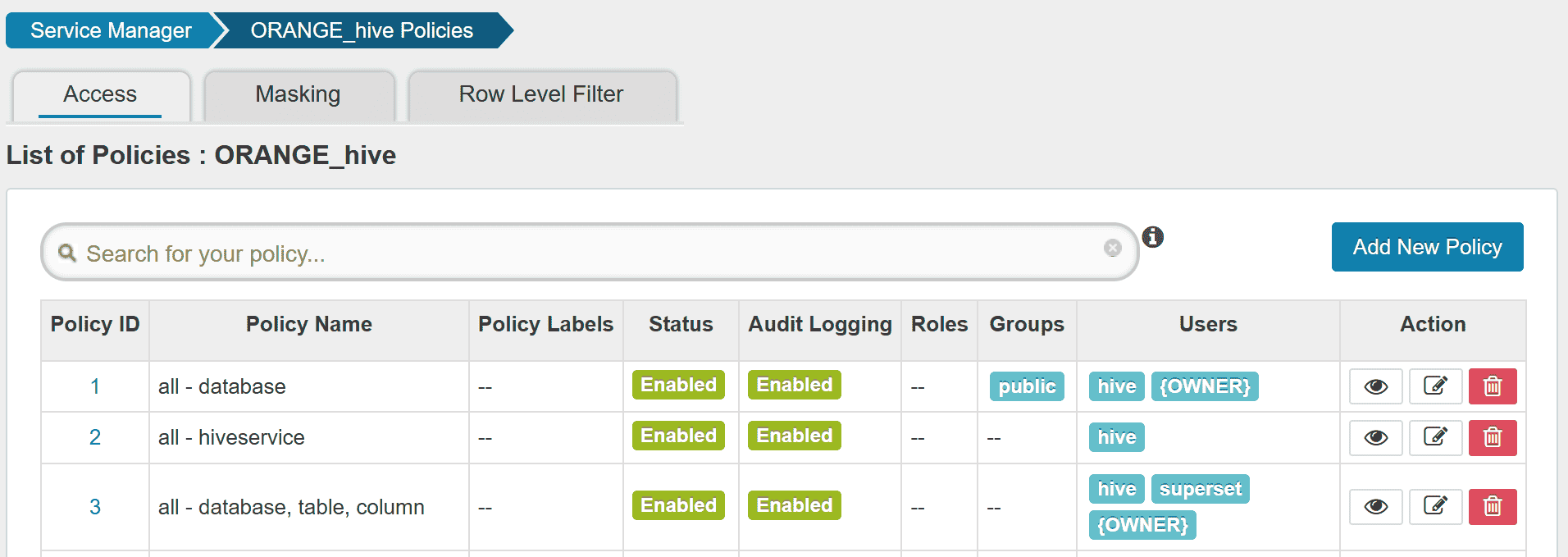
Create a Ranger service ORANGE_hive.
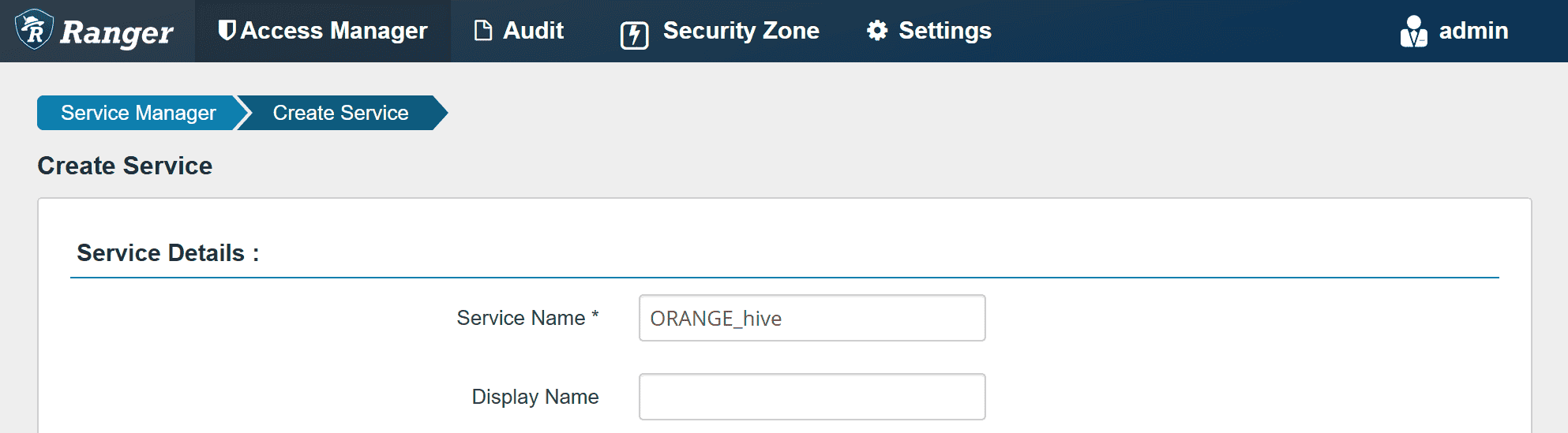
In Config Properties,
fill the JDBC URL field with:
jdbc:hive2://orange1:9852/
policy.download.auth.users should be set to the user hive, or the owner of HiveServer2.
Then Ranger can inspect metadata (such as databases, tables, users) managed by HiveServer2
while HiveServer2 can retrieve its Ranger service profile.
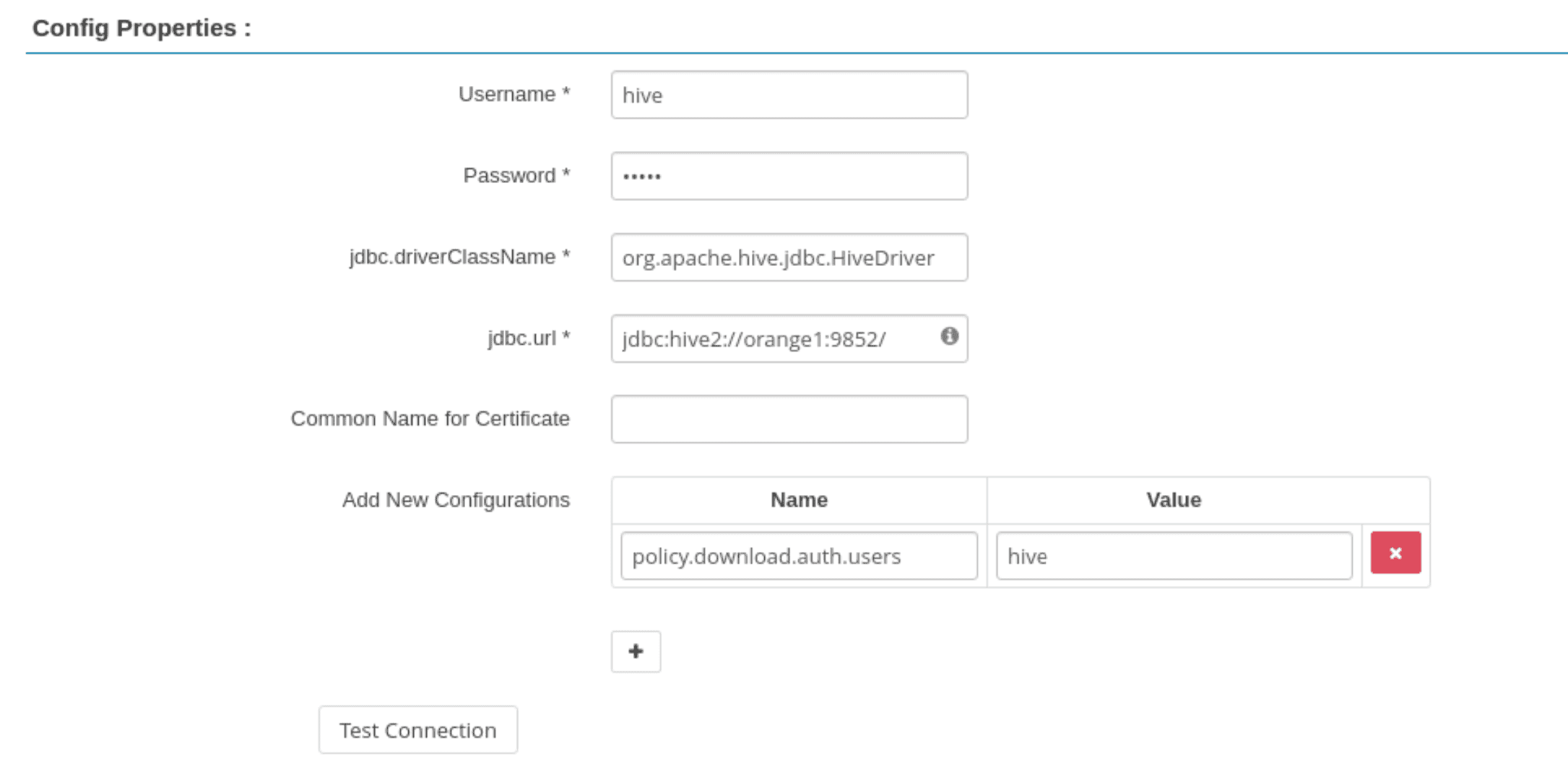
While creating the Ranger service,
the Test Connection button fails because HiveServer2 is unaware of it.
After creating the Ranger service, the button should work.
After creating the Ranger service,
HiveServer2 successfully downloads the policy for ORANGE_hive.
kubectl logs -n hivemr3 hivemr3-hiveserver2-7fbb4cb8c4-7ksrh | grep ORANGE_hive
...
2025-03-22T14:54:21,391 INFO [PolicyRefresher(serviceName=ORANGE_hive)-25] policyengine.RangerPolicyRepository: This policy engine contains 8 policy evaluators
As the last step before executing queries,
new users should be added to the Ranger policy.
For example, we can add a new user superset to allow Superset.