Single-table Queries
The default configuration of Hive on MR3 is optimized for batch and interactive queries
that involve join operations across multiple tables.
For simpler queries that analyze single tables,
the configuration key hive.optimize.reducededuplication in hive-site.xml
can make a difference.
hive.optimize.reducededuplication
Consider the following query on a single table trade_record.
SELECT shop_id, partner, COUNT(DISTINCT unique_id)
FROM trade_record
GROUP BY shop_id, partner;
The default configuration works well
if the number of distinct values of the key unique_id is relatively small.
In our example, we assume that the number is close to the total number of records.
> SELECT COUNT(*) FROM trade_record;
9769696688
> SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT unique_id) FROM trade_record;
5361347747
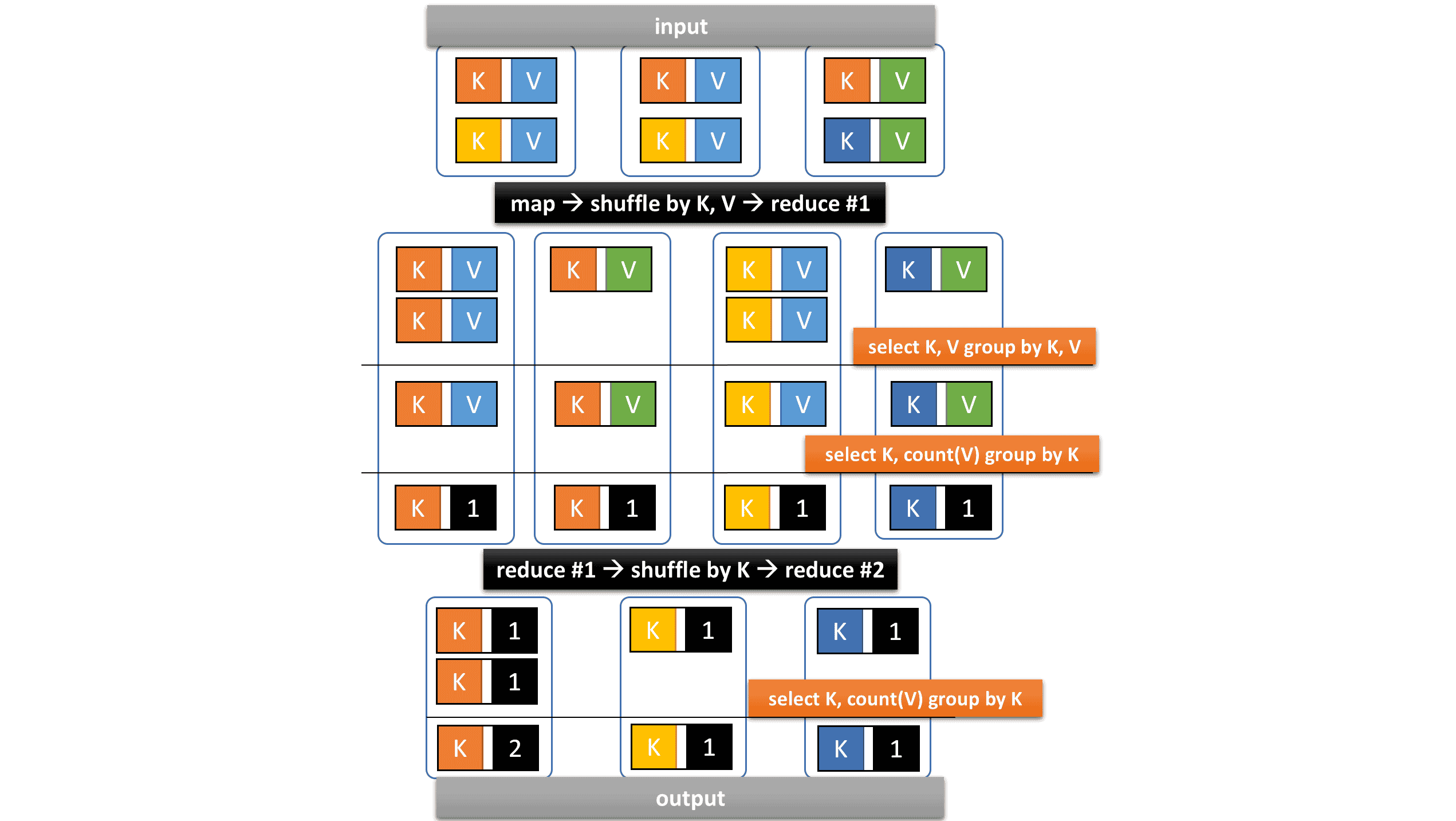
By default, the configuration key hive.optimize.reducededuplication is set to true
and Hive on MR3 produces the following query plan
where the key K corresponds to (shop_id, partner)
and the value V corresponds to unique_id.
The query plan is already optimized in that
two GROUP BY operators are executed in a single Vertex,
which, however, can become the performance bottleneck.
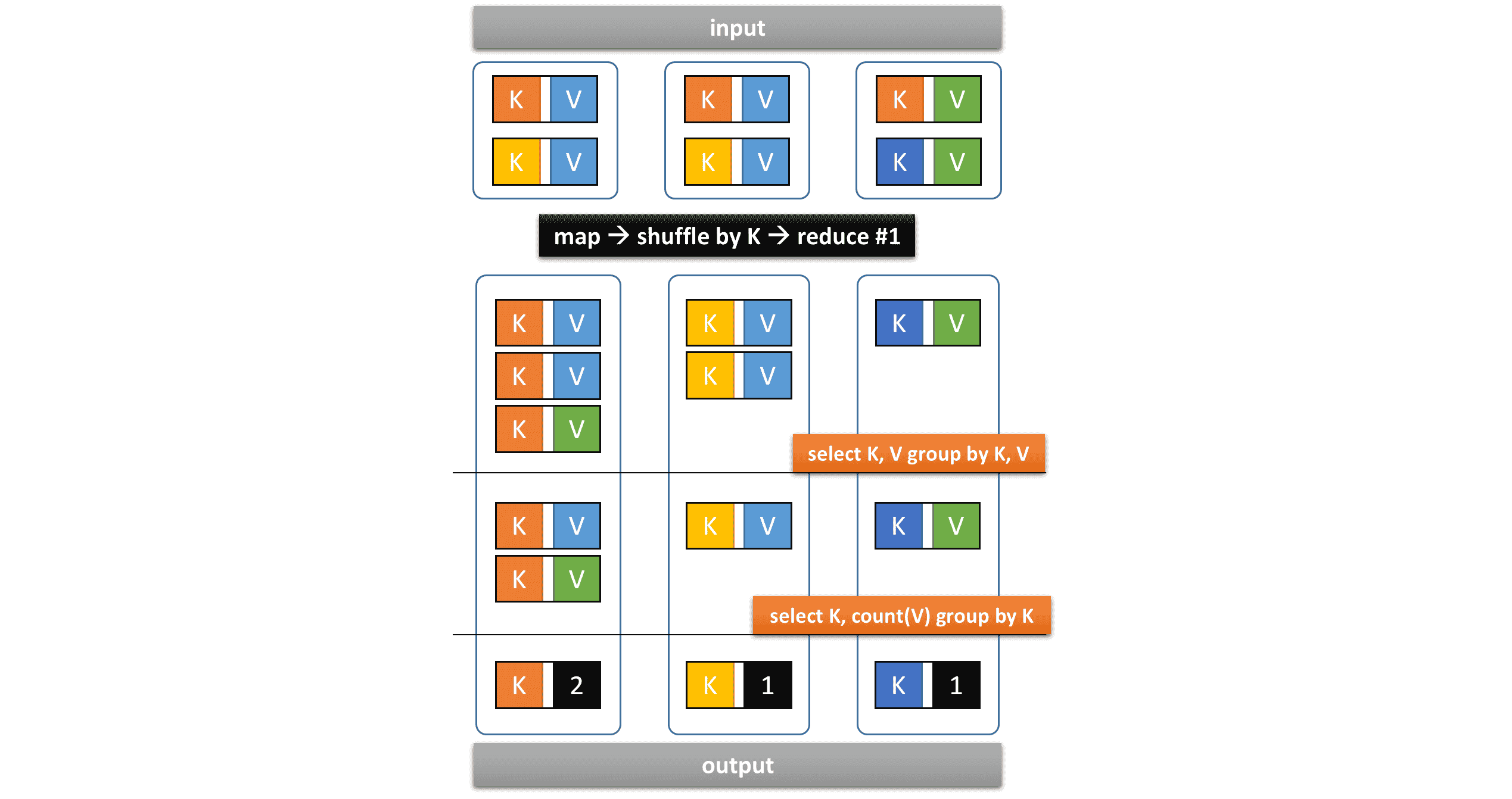
We can set hive.optimize.reducededuplication to false
in order to split the Vertex into two.
A new shuffling stage is introduced, but the total execution time may decrease
because more Tasks can be executed concurrently.