By running Ranger, we complete a Kubernetes cluster which supports data security.
We can run Ranger as a separate application (independently of Hive on MR3), so this page should be useful to anyone who wants to run Ranger on Kubernetes. If a Docker image for Ranger has already been built, download an MR3 release containing the executable scripts and skip the instruction below for building a Docker image.
$ git clone https://github.com/mr3project/mr3-run-k8s.git
$ cd mr3-run-k8s/
Building a Docker image for Ranger (Optional)
The user can use a pre-built Docker image from DockerHub (mr3project/ranger).
To build a Docker image for Ranger,
go to the installation directory of Hive on MR3 (see Installing on Kubernetes).
Set the environment variable HIVE_MYSQL_DRIVER in env.sh to a connector jar file
compatible with the database supported for Ranger.
For MySQL, Postgres, and MS SQL,
HIVE_MYSQL_DRIVER may be set to empty because the Ranger Pod either already includes or automatically downloads a compatible database connector.
$ vi env.sh
HIVE_MYSQL_DRIVER=
Collect all necessary files in the directory kubernetes/ranger by executing the script build-k8s-ranger.sh.
$ ./build-k8s-ranger.sh
downloading Solr at /tmp/solr-8.11.2.tgz
...
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESS
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Total time: 36:18 min
[INFO] Finished at: 2023-12-27T20:14:21+09:00
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
build-k8s-ranger.sh downloads a binary distribution of Apache Solr
and clones a git repository of Ranger under the directory /tmp/ranger.
Then it compiles Ranger and populates two directories:
kubernetes/ranger for building a Docker image for Ranger
and kubernetes/hive for installing the Hive plugin for Ranger.
For building Ranger, the user should use Maven 3.6.2 and Python 3 with the requests library.
If build-k8s-ranger.sh fails, check the variable SOLR_DOWNLOAD_URL
(which specifies the address of the binary distribution of Apache Solr)
in the function build_k8s_ranger of common-build-setup.sh.
The user can also change the version of Ranger and the directory $RANGER_HOME where Ranger is built.
If build-k8s-ranger.sh fails at the last step when building a Ranger distribution,
manually execute the Maven command in the directory $RANGER_HOME.
$ vi common-build-setup.sh
function build_k8s_ranger {
...
TMP_DIR=${RANGER_TMP_DIR:-/tmp}
...
SOLR_DOWNLOAD_URL=https://archive.apache.org/dist/lucene/solr/8.11.2/solr-8.11.2.tgz
...
RANGER_HOME=$TMP_DIR/ranger
...
RANGER_GIT_REV=50ad9c19e62f5aa6b2888b17437aa6fb1e2c0a36
RANGER_VERSION=2.4.0
Similarly to building a Docker image for running Hive on MR3,
the user should set an environment variable DOCKER_RANGER_IMG in kubernetes/env.sh:
$ vi kubernetes/env.sh
DOCKER_RANGER_IMG=10.1.91.17:5000/ranger:latest
DOCKER_RANGER_IMGspecifies the full name of the Docker image (including a tag) for running Ranger which may include the address of a running Docker server.
The last step is to build a Docker image from Dockerfile in the directory kubernetes/ranger
by executing kubernetes/build-ranger.sh.
The script builds a Docker image (which contains everything for running Ranger)
and registers it to the Docker server specified in kubernetes/env.sh.
If successful, the user can pull the Docker image on another node:
$ docker pull 10.1.91.17:5000/ranger
Using default tag: latest
Trying to pull repository 10.1.91.17:5000/ranger ...
latest: Pulling from 10.1.91.17:5000/ranger
...
Status: Downloaded newer image for 10.1.91.17:5000/ranger:latest
After building the Docker image for Ranger, the user should rebuild the Docker image for running Hive on MR3 because HiveServer2 needs the Hive plugin for Ranger. Below we describe how to run Ranger.
Configuring the Pod for Ranger
The following files specify how to configure Kubernetes objects for Ranger:
└── kubernetes
├── env.sh
├── ranger-key
└── yaml
├── namespace.yaml
├── ranger-service.yaml
├── ranger.yaml
├── workdir-pvc-ranger.yaml
└── workdir-pv-ranger.yaml
We assume that Ranger belongs to the same namespace as HiveServer2, and reuse namespace.yaml.
Ranger uses workdir-pvc-ranger.yaml and workdir-pv-ranger.yaml
which can be configured similarly to workdir-pvc.yaml and workdir-pv.yaml.
The PersistentVolume should be writable to the user with UID 1000
(which is specified in kubernetes/ranger/Dockerfile).
The user should set the following environment variable in kubernetes/env.sh.
$ vi kubernetes/env.sh
CREATE_RANGER_SECRET=true
CREATE_RANGER_SECRETspecifies whether or not to create a Secret from keytab files in the directorykubernetes/ranger-key. Usually it should be set to true whether Kerberos is used for authentication or not (because ofkubernetes/ranger-key/install.properties).
ranger-service.yaml
This file creates a Service for exposing Ranger to the outside of the Kubernetes cluster.
The user should specify an IP address with a valid host name and three port numbers for Ranger
so that both the administrator user from the outside and HiveServer2 from the inside can connect to it using the host name.
Usually there is no need to change the three targetPort fields which specify port numbers internal to the Ranger Pod.
$ vi kubernetes/yaml/ranger-service.yaml
ports:
- name: ranger-admin-http
protocol: TCP
port: 6080
targetPort: 6080
- name: ranger-admin-https
protocol: TCP
port: 6182
targetPort: 6182
- name: solr
protocol: TCP
port: 6083
targetPort: 6083
externalIPs:
- 10.1.91.41
In our example, we use 10.1.91.41:6080 as the HTTP address and 10.1.91.41:6182 as the HTTPS address of Ranger. Another address 10.1.91.41:6083 is reserved for the internal communication between Ranger and Solr. The user should make sure that the IP address exists and is not already taken.
ranger.yaml
This file creates a Pod for running Ranger.
Internally the Pod runs two containers (for Ranger itself and for Solr) in parallel.
The user should update the spec/hostAliases field and the spec/containers section.
- The
spec/hostAliasesfield lists aliases for hosts that may not be found in the default DNS. Usually it suffices to include three hosts: 1) the host running MySQL for Ranger outside the Kubernetes cluster; 2) the host running HiveServer2 inside the Kubernetes cluster; 3) the host running Ranger inside the Kubernetes cluster. In our example,red0is the host running MySQL for Ranger andindigo20is the host name assigned to HiveServer2 and Ranger.$ vi kubernetes/yaml/ranger.yaml hostAliases: - ip: "10.1.91.4" hostnames: - "red0" - ip: "10.1.91.41" hostnames: - "indigo20" - The
imagefield in thespec/containerssection should match the Docker image specified byDOCKER_RANGER_IMGinkubernetes/env.sh. - The
resources/requestsandresources/limitsspecify the resources to to be allocated to the Ranger container and the Solr container. - The
ports/containerPortfields should match the port numbers specified in thetargetPortfields inranger-service.yaml.
$ vi kubernetes/yaml/ranger.yaml
spec:
containers:
- image: 10.1.91.17:5000/ranger
name: solr
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1
memory: 4Gi
limits:
cpu: 1
memory: 4Gi
ports:
- containerPort: 6083
protocol: TCP
- image: 10.1.91.17:5000/ranger
name: ranger
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1
memory: 4Gi
limits:
cpu: 1
memory: 4Gi
ports:
- containerPort: 6080
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 6182
protocol: TCP
Configuring Ranger
The following files specify how to configure Ranger:
└── kubernetes
├── ranger-conf
│ ├── core-site.xml
│ ├── krb5.conf
│ ├── ranger-admin-site.xml.append
│ ├── ranger-log4j.properties
│ ├── solr-core.properties
│ ├── solr-elevate.xml
│ ├── solr-log4j2.xml
│ ├── solr-managed-schema
│ ├── solr-security.json
│ ├── solr-solrconfig.xml
│ └── solr-solr.xml
└── ranger-key
├── install.properties
└── solr.in.sh
Because of lack of detailed documentation on configuring Ranger, the user is strongly advised to run Ranger initially with minimal changes to the configuration files in the MR3 release (which should work okay in a typical Kubernetes cluster). After getting Ranger up and running, the user can incrementally adjust the configuration to suit particular needs. Otherwise the user might have to fix the configuration by reading the source code of Ranger.
We assume that SSL is not enabled.
Set SOLR_SSL_ENABLED to false in kubernetes/ranger-key/solr.in.sh.
To enable SSL, see Enabling SSL.
$ vi kubernetes/ranger-key/solr.in.sh
SOLR_SSL_ENABLED=false
When running Ranger without Kerberos, SSL should not be enabled.
When using Kerberos authentication,
we recommend the user to create three Kerberos keytab files with the following names.
In our example, we assume that indigo20 is the host name assigned to the Service for Ranger service and that RED is the Kerberos realm.
The user should copy the keytab files in the directory kubernetes/ranger-key.
rangeradmin.keytabwith admin service principalrangeradmin/indigo20@RED. The instance (e.g.,indigo20) must match the host name for Ranger.spnego.service.keytabwith SPNEGO service principalHTTP/indigo20@RED. The primary must beHTTPand the instance (e.g.,indigo20) must match the host name for Ranger.rangerlookup.keytabwith lookup principalrangerlookup@RED. An ordinary principal (without an instance) is okay to use.
core-site.xml
Set the configuration key hadoop.security.authentication to kerberos to enable Kerberos authentication.
$ vi kubernetes/ranger-conf/core-site.xml
<property>
<name>hadoop.security.authentication</name>
<value>kerberos</value>
</property>
Set it to simple to disable Kerberos authentication.
$ vi kubernetes/ranger-conf/core-site.xml
<property>
<name>hadoop.security.authentication</name>
<value>simple</value>
</property>
krb5.conf for Kerberos authentication
This file should contains the information for Kerberos configuration.
Usually it suffices to use a copy of kubernetes/conf/krb5.conf.
The user may have to comment out the variable renew_lifetime if an error Message stream modified occurs
(as explained in Configuring Pods).
ranger-admin-site.xml.append
When using Kerberos authentication,
set the configuration key xasecure.audit.jaas.Client.option.principal
to admin service principal.
$ vi kubernetes/ranger-conf/ranger-admin-site.xml.append
<property>
<name>xasecure.audit.jaas.Client.option.principal</name>
<value>rangeradmin/indigo20@RED</value>
</property>
solr-security.json
This file sets the configuration for authentication and authorization in Solr.
When using Kerberos authentication,
the user-role section should specify the service principal for HiveServer2 and the admin service principal for Ranger.
$ vi kubernetes/ranger-conf/solr-security.json
"authentication": {
"class": "org.apache.solr.security.KerberosPlugin"
},
"authorization": {
...
"user-role": {
"hive/indigo20@RED": "updater",
"rangeradmin/indigo20@RED": "reader",
}
}
If Kerberos is not used, set as follows:
$ vi kubernetes/ranger-conf/solr-security.json
{
"authentication": {
"blockUnknown": false,
"class": "solr.BasicAuthPlugin",
"credentials":{
"solr":"IV0EHq1OnNrj6gvRCwvFwTrZ1+z1oBbnQdiVC3otuq0= Ndd7LKvVBAaZIF0QAVi1ekCfAJXr1GGfLtRUXhgrF8c="
}
},
"authorization": {
"class": "solr.RuleBasedAuthorizationPlugin"
}
}
Since authentication/blockUnknown is set to false,
Solr accepts audit requests without credentials.
(Ranger does not use the credentials which correspond to user solr and password solrRocks.)
install.properties
-
DB_FLAVORandSQL_CONNECTOR_JARshould match the database connector jar file.$ vi kubernetes/ranger-key/install.properties DB_FLAVOR=MYSQL SQL_CONNECTOR_JAR=/opt/mr3-run/lib/mysql-connector-java-8.0.28.jar # for PostgreSQL: # DB_FLAVOR=POSTGRES # SQL_CONNECTOR_JAR=/opt/mr3-run/lib/postgresql-42.3.2.jar # for MS SQL: # DB_FLAVOR=MSSQL # SQL_CONNECTOR_JAR=/opt/mr3-run/lib/mssql-jdbc-10.2.0.jre8.jarWhen using a MySQL server, Ranger automatically downloads a MySQL connector from
https://cdn.mysql.com/Downloads/Connector-J/mysql-connector-java-8.0.28.tar.gzandSQL_CONNECTOR_JARcan be set as shown above.If a custom database connector should be used, the user can copy a connector jar file to a subdirectory of the PersistentVolume and set
SQL_CONNECTOR_JARto point to the file (e.g.,SQL_CONNECTOR_JAR=/opt/mr3-run/ranger/work-dir/lib/mysql-connector-java-8.0.12.jar). In this way, Ranger can use the custom database connector provided by the user. If the Docker image for Ranger already contains a compatible database connector, the PersistentVolume is not used. -
db_root_useranddb_root_passwordshould be set to the ID and password of the root user of MySQL for Ranger.$ vi kubernetes/ranger-key/install.properties db_root_user=root db_root_password=passwd -
db_hostshould be set to the IP address or the host name of MySQL for Ranger.$ vi kubernetes/ranger-key/install.properties db_host=indigo0 -
db_passwordspecifies a password for the userrangeradmin.$ vi kubernetes/ranger-key/install.properties db_password=password -
RANGER_ADMIN_LOG_DIRspecifies the directory for logging. By default, Ranger uses a local directory mounted with an emptyDir volume.$ vi kubernetes/ranger-key/install.properties RANGER_ADMIN_LOG_DIR=/opt/mr3-run/ranger/work-local-dir/log/ranger-admin -
Set the variable
audit_solr_urlsto the address for the configuration keyranger.audit.solr.urls. Remove (do not just set to empty) two variables related to authentication for auditing:audit_solr_userandaudit_solr_password.$ vi kubernetes/ranger-key/install.properties audit_solr_urls=http://indigo20:6083/solr/ranger_audits # audit_solr_user # audit_solr_password -
policymgr_external_urlshould be set to the Ranger admin URL.policymgr_http_enabledshould be set to true.$ vi kubernetes/ranger-key/install.properties policymgr_external_url=http://indigo20:6080 policymgr_http_enabled=true -
When using Kerberos authentication, set the following variables to Kerberos principals.
$ vi kubernetes/ranger-key/install.properties admin_principal=rangeradmin/indigo20@RED spnego_principal=HTTP/indigo20@RED lookup_principal=rangerlookup@RED
solr.in.sh
When using Kerberos authentication,
the environment variable SOLR_AUTHENTICATION_OPTS should use
the host running Ranger, the SPNEGO service principal, and its service keytab.
$ vi kubernetes/ranger-key/solr.in.sh
SOLR_AUTH_TYPE="kerberos"
SOLR_AUTHENTICATION_OPTS="\
-Djava.security.krb5.conf=/opt/mr3-run/ranger/conf/krb5.conf \
-Dsolr.kerberos.cookie.domain=indigo20 \
-Dsolr.kerberos.principal=HTTP/indigo20@RED \
-Dsolr.kerberos.keytab=/opt/mr3-run/ranger/key/spnego.service.keytab"
If Kerberos is not used, set as follows:
$ vi kubernetes/ranger-key/solr.in.sh
SOLR_AUTH_TYPE="basic"
SOLR_AUTHENTICATION_OPTS="-Dbasicauth=solr:solrRocks"
Running Ranger
In order to run Ranger, the user can execute the script kubernetes/run-ranger.sh:
$ kubernetes/run-ranger.sh
namespace/hivemr3 created
persistentvolume/workdir-pv-ranger created
persistentvolumeclaim/workdir-pvc-ranger created
configmap/hivemr3-ranger-conf-configmap created
secret/hivemr3-ranger-secret created
deployment/hivemr3-ranger created
service/ranger created
Executing the script kubernetes/run-ranger.sh starts a Ranger Pod (consisting of two containers) in a moment:
$ kubectl get -n hivemr3 pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hivemr3-ranger-2q9wv 2/2 Running 0 33s
The user can check the log of the Ranger Pod to see if Ranger has successfully started:
$ kubectl logs -n hivemr3 hivemr3-ranger-2q9wv ranger
2020-10-09 07:19:37,935 --------- Running Ranger PolicyManager Web Application Install Script ---------
2020-10-09 07:19:37,942 [I] uname=Linux
2020-10-09 07:19:37,947 [I] hostname=hivemr3-ranger-2q9wv
2020-10-09 07:19:37,961 [I] DB_FLAVOR=MYSQL
...
Installation of Ranger PolicyManager Web Application is completed.
Starting Apache Ranger Admin Service
Apache Ranger Admin Service with pid 1661 has started.
Then the user can connect to the Ranger webpage at the address specified by the configuration key ranger.externalurl.
The default ID/password is admin/rangeradmin1
(where the password is given in kubernetes/ranger-key/install.properties):
$ vi kubernetes/ranger-key/install.properties
rangerAdmin_password=rangeradmin1
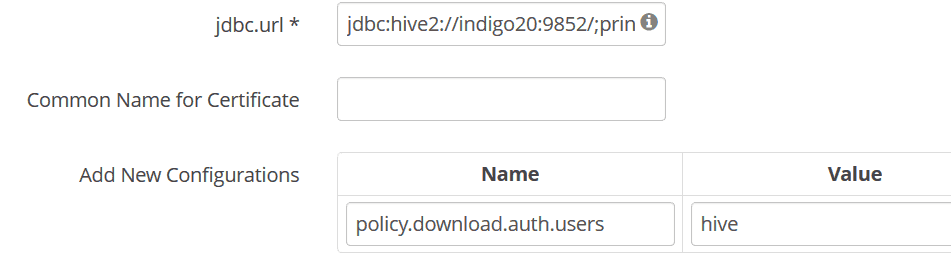
After starting Ranger, connect to the Ranger webpage and create a Ranger service specified in kubernetes/conf/ranger-hive-security.xml.
Then fill the JDBC URL (e.g., jdbc:hive2://indigo20:9852/;principal=hive/indigo20@RED;)
and set policy.download.auth.users to the user hive, or the owner of HiveServer2.
In this way, Ranger can inspect metadata (such as databases, tables, users) managed by HiveServer2 while HiveServer2 can retrieve its Ranger service profile.
Reconfiguring and running HiveServer2 after starting Ranger
After starting Ranger, HiveServer2 should be reconfigured so as to communicate with Ranger for checking data security.
If the Ranger plugin is missing in the directory kubernetes/hive/hive/apache-hive/lib,
the user should rebuild the Docker image for running Hive on MR3 before restarting HiveServer2.
(The MR3 release already includes the Ranger plugin.)
kubernetes/yaml/hive.yaml
The spec/hostAliases field should include the host running Ranger inside the Kubernetes cluster.
kubernetes/conf/hive-site.xml
The following configuration keys should be set:
$ vi kubernetes/conf/hive-site.xml
<property>
<name>hive.security.authenticator.manager</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.security.SessionStateUserAuthenticator</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.authorization.manager</name>
<value>org.apache.ranger.authorization.hive.authorizer.RangerHiveAuthorizerFactory</value>
</property>
The user may choose to set hive.server2.enable.doAs to true because enabling impersonation is orthogonal to using Ranger.
kubernetes/conf/ranger-hive-security.xml
The configuration key ranger.plugin.hive.policy.rest.url should use the host name assigned to Ranger.
Note that the port number should match the field port, not targetPort, in yaml/ranger-service.yaml because HiveServer2 connects via the Service that exposes Ranger to the outside of the Kubernetes cluster.
$ vi kubernetes/conf/ranger-hive-security.xml
<property>
<name>ranger.plugin.hive.policy.rest.url</name>
<value>http://indigo20:6080</value>
</property>
The configuration key ranger.plugin.hive.service.name should use the Ranger service for HiveServer2:
$ vi kubernetes/conf/ranger-hive-security.xml
<property>
<name>ranger.plugin.hive.service.name</name>
<value>INDIGO_hive</value>
</property>
kubernetes/conf/ranger-hive-audit.xml
The configuration key xasecure.audit.destination.solr.urls should use the host name assigned to Ranger.
$ vi kubernetes/conf/ranger-hive-audit.xml
<property>
<name>xasecure.audit.destination.solr.urls</name>
<value>http://indigo20:6083/solr/ranger_audits</value>
</property>
Troubleshooting
1. HiveServer2 throws NullPointerException when trying to download Ranger policies, and Beeline cannot execute queries.
2020-10-08T12:23:08,872 ERROR [Thread-6] util.PolicyRefresher: PolicyRefresher(serviceName=ORANGE_hive): failed to refresh policies. Will continue to use last known version of policies (-1)
com.sun.jersey.api.client.ClientHandlerException: java.lang.RuntimeException: java.lang.NullPointerException
...
Caused by: java.lang.NullPointerException
0: jdbc:hive2://orange1:9852/> use tpcds_bin_partitioned_orc_1003;
Error: Error while compiling statement: FAILED: HiveAccessControlException Permission denied: user [gitlab-runner] does not have [USE] privilege on [tpcds_bin_partitioned_orc_1003] (state=42000,code=40000)
The error disappears after setting policy.download.auth.users to include the user of HiveServer2 in the Config Properties panel.
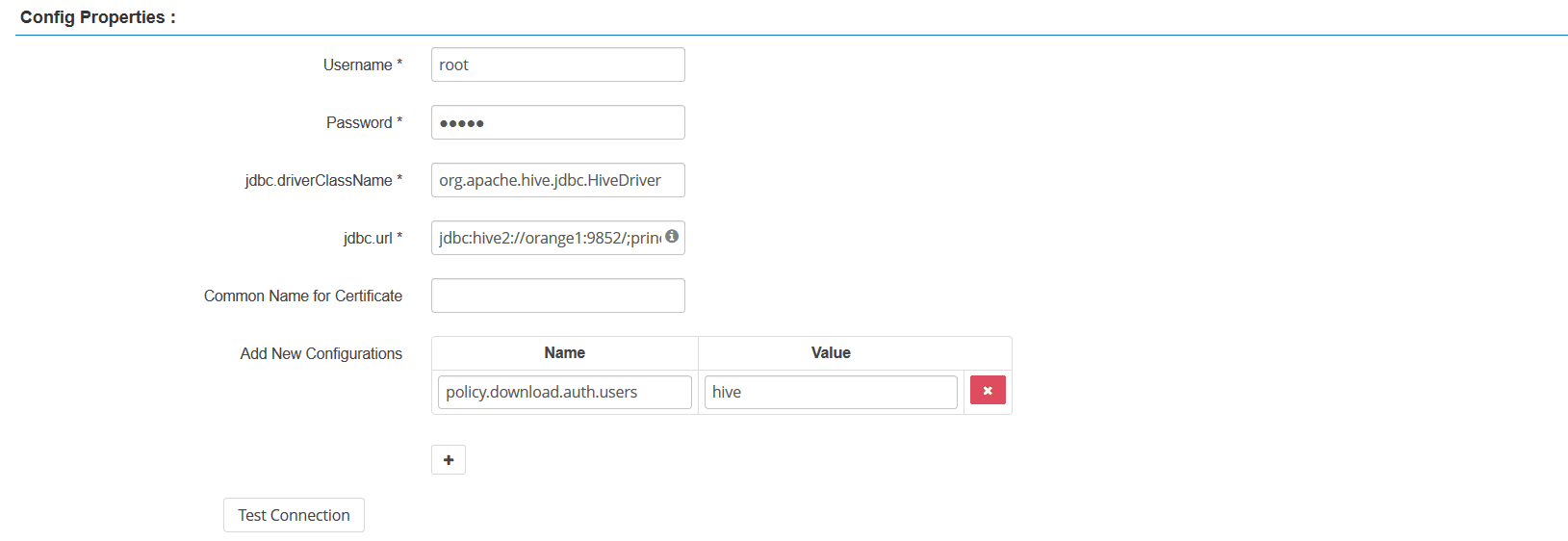
2. Test Connection fails in the Config Properties panel.
Check if the jdbc.url field is set properly.
Examples:
jdbc:hive2://indigo20:9852/when neither Kerberos nor SSL is used.jdbc:hive2://indigo20:9852/;principal=hive/indigo20@RED;when Kerberos is used.jdbc:hive2://indigo20:9852/;principal=hive/indigo20@RED;ssl=true;sslTrustStore=/opt/mr3-run/ranger/key/hivemr3-ssl-certificate.jks;when both Kerberos and SSL are used.
3. Apache Ranger Admin Service fails to start.
In order to find out the cause of the failure, check out the file catalina.out
available in the Ranger container (not the Solr container) inside the Ranger Pod.
In the following example, Admin Service fails to start because a wrong Kerberos keytab file is provided.
$ kubectl -n hivemr3 logs hivemr3-ranger-cbq29 ranger
...
Installation of Ranger PolicyManager Web Application is completed.
Starting Apache Ranger Admin Service
Apache Ranger Admin Service failed to start!
$ kubectl exec -it -n hivemr3 hivemr3-ranger-0 -c ranger /bin/bash;
root@hivemr3-ranger-0:/opt/mr3-run/ranger# cat work-local-dir/log/ranger-admin/catalina.out
…
SEVERE: Tomcat Server failed to start:java.io.IOException: Login failure for rangeradmin/orange1@PL from keytab /opt/mr3-run/ranger/key/rangeradmin.keytab
java.io.IOException: Login failure for rangeradmin/orange1@PL from keytab /opt/mr3-run/ranger/key/rangeradmin.keytab
...
Caused by: java.security.GeneralSecurityException: Checksum failed
...