Hive supports auto parallelism which reduces the number of Tasks in a Reduce Vertex dynamically after analyzing the output of its source Vertexes. In the following example, several Reduce Vertexes find their number of Tasks decreasing from 1009 to 253:
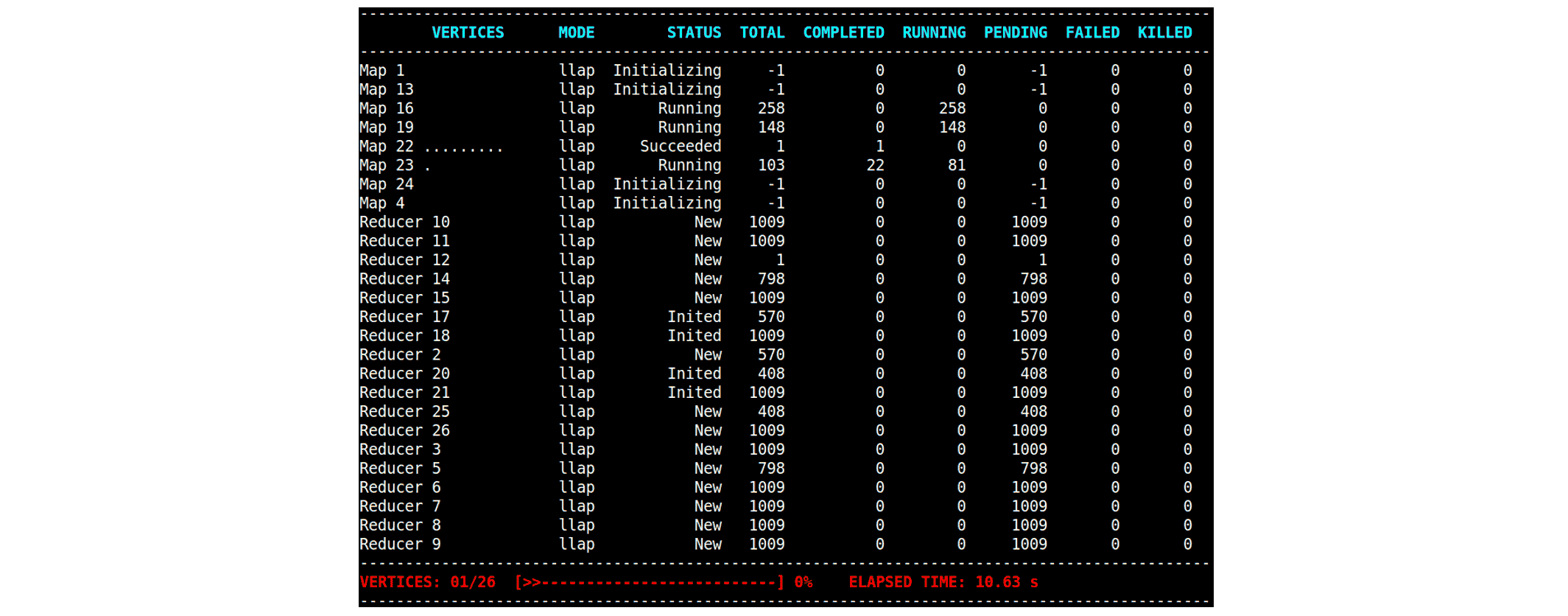
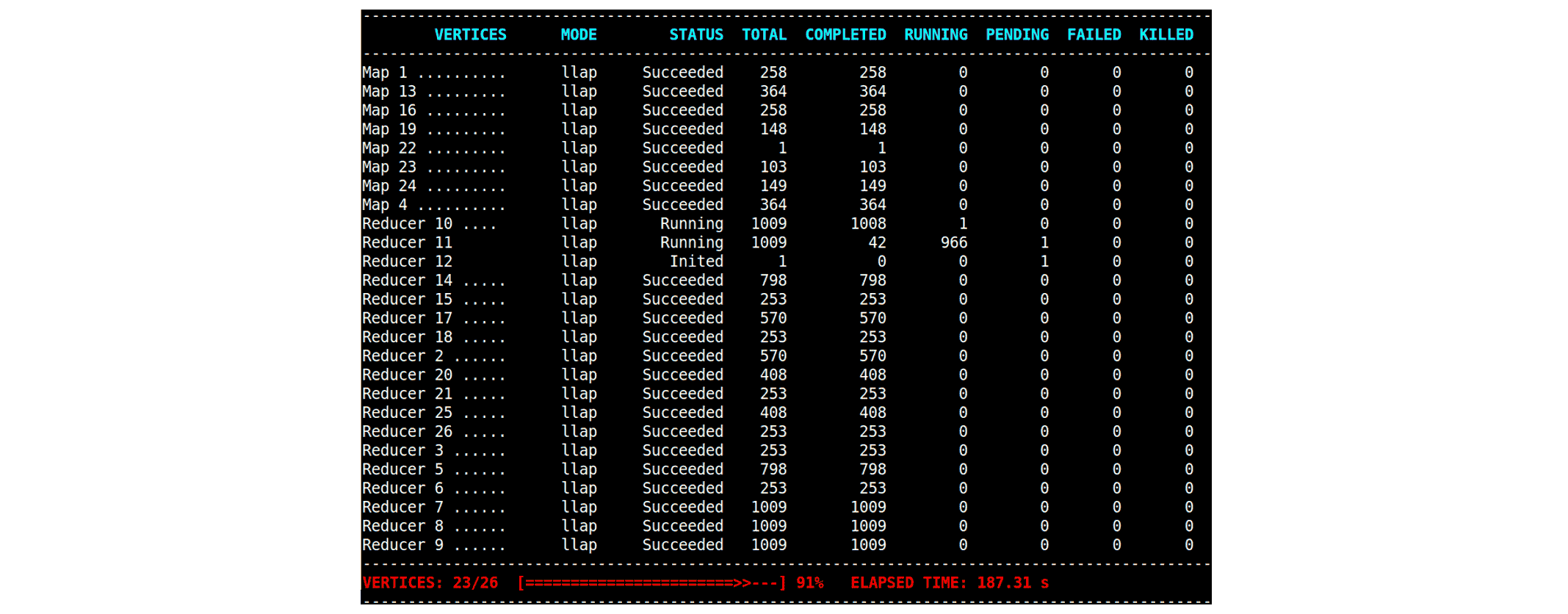
By launching fewer Tasks for Reduce Vertexes, Hive makes a better utilization of resources, especially in concurrent environments in which many queries compete for resources. Moreover enabling auto parallelism has practically no negative impact on the execution time.
Auto parallelism in Hive on MR3
Hive on MR3 provides a more faithful implementation of auto parallelism in comparison with Hive on Tez and Hive-LLAP, which allow auto parallelism only in limited circumstances.
For example, Hive on MR3 can apply auto parallelism on those Vertexes with ONE_TO_ONE incoming or outgoing edges,
whereas Hive on Tez and Hive-LLAP skip such Vertexes in applying auto parallelism.
In the following diagram, Reducer 7 to 11 (in green rectangles) are all connected via ONE_TO_ONE edges, and Hive on MR3 makes sure that their number of Tasks remains the same
after applying auto parallelism (from 1009 to 253):
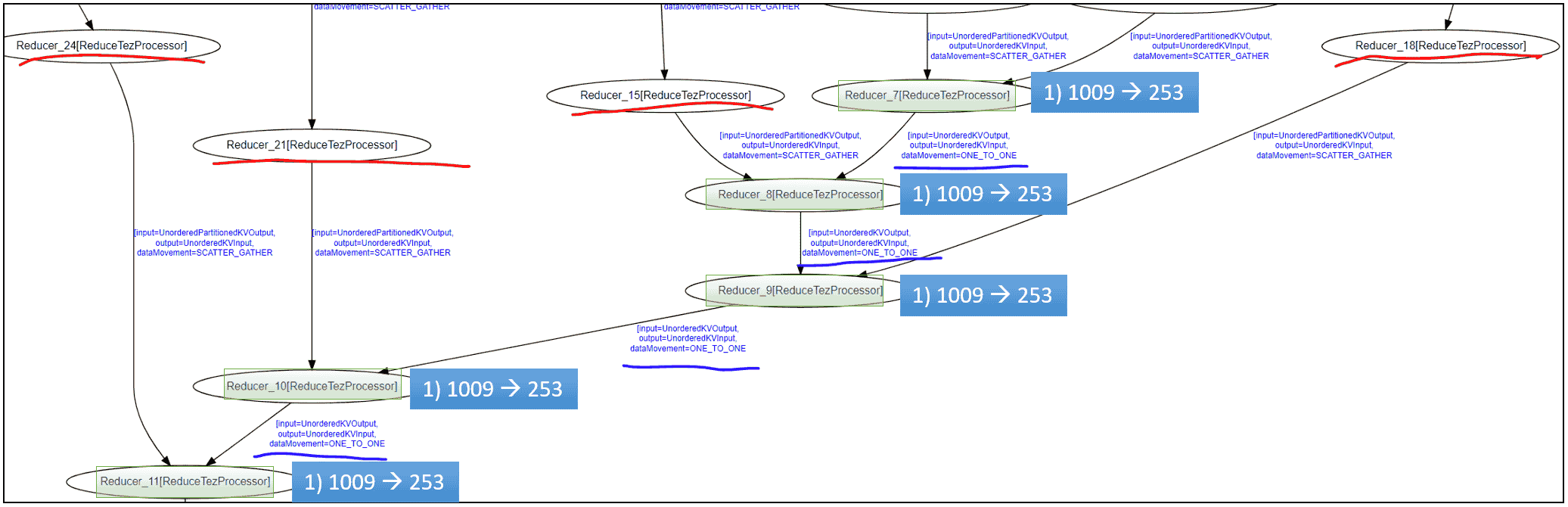
Auto parallelism in Hive on MR3 also allows upstream Tasks to be mapped to downstream Tasks (of a Reduce Vertex) according to the statistics of their output rather than their Task indexes. For example, upstream Tasks with small output may be grouped together to be mapped to a single downstream Task while an upstream Task with large output may be mapped to its own unique downstream Task. In this way, Hive on MR3 can mitigate the problem of skews in the distribution of output from upstream Tasks.
Enabling auto parallelism
In order to enable auto parallelism, set tez.shuffle-vertex-manager.enable.auto-parallel to true in tez-site.xml.
(From MR3 1.3, Hive on MR3 enables or disables auto parallelism
according to the result of compiling queries by overriding tez.shuffle-vertex-manager.enable.auto-parallel,
so it can be set to false.)
tez.shuffle-vertex-manager.use-stats-auto-parallelism should be set to true in order to use the statistics of output from upstream Tasks.
See Configuring Tez Runtime for additional configuration keys.