Autoscaling in MR3
MR3 implements a mechanism of requesting new ContainerWorkers and emptying existing ContainerWorkers in order to assist autoscaling in cloud environments. It measures the aggregate utilization of the cluster based on the memory consumed by TaskAttempts over a certain period of time, and performs two kinds of operations in order to keep the aggregate utilization within a certain range.
- Scale-out: When the aggregate utilization exceeds a threshold, MR3 tries to obtain new ContainerWorkers by sending requests to the cluster management system such as Hadoop and Kubernetes.
- Scale-in: When the aggregate utilization decreases past a certain point, MR3 empties a certain number of nodes so that the cluster management system can quickly reclaim these nodes.
In the case of scale-out, the cluster management system usually responds by adding new hosts where new ContainerWorkers can start. In the case of scale-in, MR3 removes all ContainerWorkers from those nodes selected for reclamation, and does not try to allocate new ContainerWorkers until the scale-in operation completes. Note that the unit of scale-out is ContainerWorkers whereas the unit of scale-in is nodes:
- For scale-out, the autoscaling mechanism of MR3 is agnostic to the underlying system and thus can send only requests of new ContainerWorkers, not new nodes.
- For scale-in, MR3 assumes that the underlying system can detect idle nodes.
In general, MR3 does not know how many ContainerWorkers can fit in a single node. Moreover nodes can be added with different capabilities in terms of memory and CPU cores, and MR3 should not make any assumption on capabilities of individual nodes.
Configuring autoscaling
The user can enable autoscaling by setting the configuration key mr3.enable.auto.scaling to true.
At any point, the scheduler for each ContainerGroup is in one of the three states: STABLE, SCALE_OUT, and SCALE_IN.
STABLE: Currently the aggregate utilization is stable and requires neither scale-out nor scale-in.SCALE_OUT: The scheduler has sent requests for new ContainerWorkers and is waiting for responses from the cluster management system.SCALE_IN: The scheduler has emptied some nodes and is waiting for a fixed period of time.
The following diagram shows the overall state transition in autoscaling.
The constants in the diagram are specified by configuration keys in mr3-site.xml.
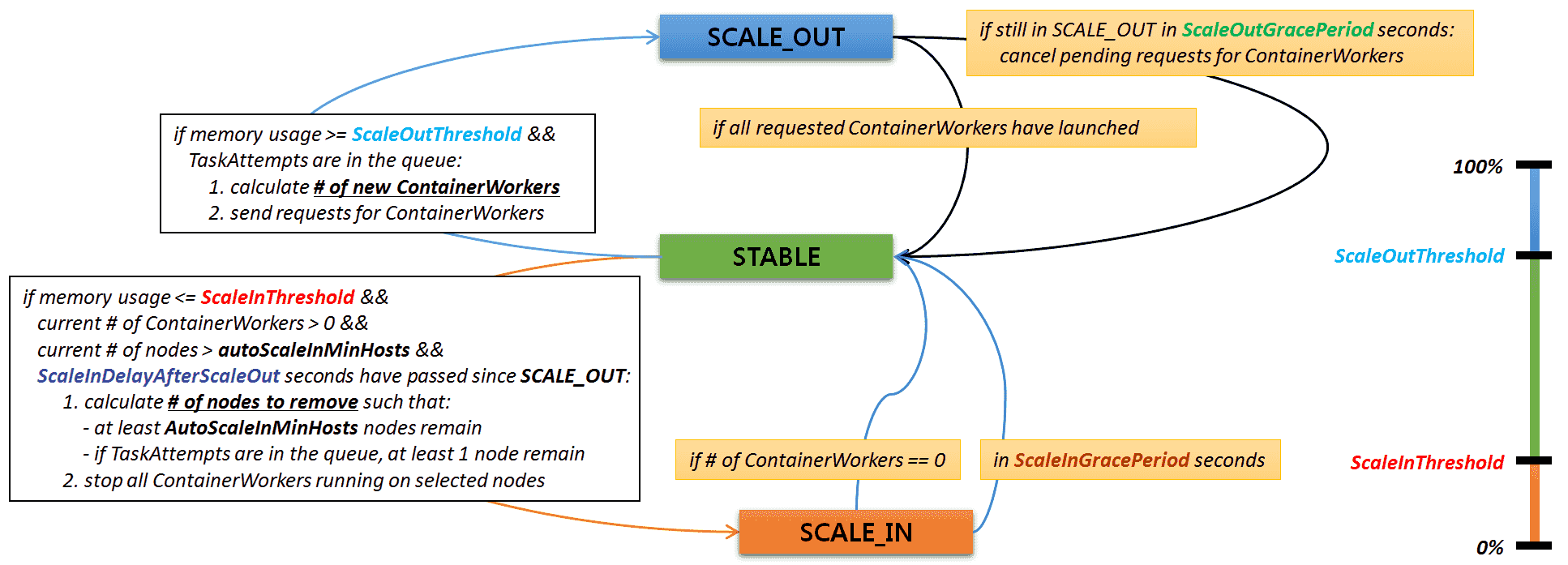
- ScaleOutThreshold =
mr3.auto.scale.out.threshold.percent. Minimum percentage of memory usage to trigger scale-out. - ScaleOutGracePeriod =
mr3.auto.scale.out.grace.period.secs. Cooldown period in seconds after triggering scale-out. The cooldown period should be much longer than the average time for completing a scale-out operation. For example, if it takes about 3 minutes to create and initialize a new worker node on Amazon EKS,mr3.auto.scale.out.grace.period.secscan be set to 360 (equivalent to 6 minutes). If the cooldown period is too short, MR3 may prematurely cancel the provisioning of worker nodes. - ScaleInDelayAfterScaleOut =
mr3.auto.scale.in.delay.after.scale.out.secs. Minimum time in seconds to wait after leaving scale-out before triggering scale-in. - ScaleInThreshold =
mr3.auto.scale.in.threshold.percent. Maximum percentage of memory usage to trigger scale-in. - AutoScaleInMinHosts =
mr3.auto.scale.in.min.hosts. Minimum number of nodes that should remain when performing scale-in. - ScaleInGracePeriod =
mr3.auto.scale.in.grace.period.secs. Cooldown period in seconds after triggering scale-in.
Approximating the aggregate utilization
MR3 approximates the aggregate utilization of the cluster by calculating memory usage.
At a regular interval specified by the configuration key mr3.check.memory.usage.event.interval.secs,
MR3 measures the fraction of memory consumed by TaskAttempts in ContainerWorkers.
For example, if there are 10 ContainerWorkers with 32GB of memory allocated for TaskAttempts while a total of 40 TaskAttempts of 4GB each are running,
we obtain 40 * 4 / 10 * 32 = 50%.
Then MR3 calculates the memory usage by accumulating all measurements over the past time window specified by the configuration key mr3.memory.usage.check.window.length.secs,
either taking the average or the maximum (specified by the configuration key mr3.memory.usage.check.scheme).
As a minor improvement to achieve fast scale-out,
MR3 excludes those measurements taken when no ContainerWorkers are running (e.g., right after the cluster starts)
and those measurements in the head of the time window with no TaskAttempts (e.g, after a long idle period).
Scale-in and scale-out
When MR3 triggers a scale-in operation, it does not immediately terminate all ContainerWorkers running in nodes selected for reclamation
(if the configuration key mr3.auto.scale.in.wait.dag.finished is set to true).
This is because these ContainerWorkers may hold intermediate data that are to be fetched by remote TaskAttempts of currently active DAGs.
Thus it continues to make use to these ContainerWorkers (e.g., by sending new TaskAttempts) until the currently active DAGs all complete.
In the actual implementation of MR3, they are set to terminate themselves when the currently active DAGs all complete.
The number of ContainerWorkers to request for scale-out and the number of nodes to empty for scale-in are set by the following configuration keys in mr3-site.xml:
mr3.auto.scale.out.num.initial.containerswith a default value of 0. It is used for fast scale-out when the current number of ContainerWorkers is zero (e.g., when creating fresh ContainerWorkers before executing the first DAG).mr3.auto.scale.out.num.increment.containerswith a default value of 0. It is used when some ContainerWorkers are currently running.mr3.auto.scale.in.num.decrement.hostswith a default value of 0
If these keys are set to zero, MR3 calculates the number of ContainerWorkers/hosts based on the difference between the current memory usage and ScaleOutThreshold/ScaleInThreshold.
On Kubernetes, the user can set a limit on the total resources for all ContainerWorker Pods with the following configuration keys:
mr3.k8s.worker.total.max.memory.gbspecifies the maximum memory in GB for all ContainerWorker Pods.mr3.k8s.worker.total.max.cpu.coresspecifies the maximum number of cores for all ContainerWorker Pods.