DaemonTasks for daemon services
A DaemonTask is a special type of Task which automatically starts TaskAttempts, called DaemonTaskAttempt, whenever new ContainerWorkers are created from its ContainerGroup. It is intended for executing a service in the background for all ordinary TaskAttempts, called WorkerTaskAttempts, and does not constitute any part of specific MR3 DAGs. Here are three examples of using DaemonTasks:
- The shuffle handler in the ASM runtime is implemented as a DaemonTask which is responsible for sending and receiving intermediate results between ContainerWorkers for all MR3 jobs.
- Hive on MR3 uses a DaemonTask to run the LLAP (Low Latency Analytical Processing) I/O service directly inside ContainerWorkers.
- Hive on MR3 can run its own shuffle handler as a DaemonTask, thus eliminating the need for an external shuffle service.
By allowing the user to attach custom DaemonTasks to ContainerGroups, MR3 facilitates the implementation of new services running in the background, or daemon services.
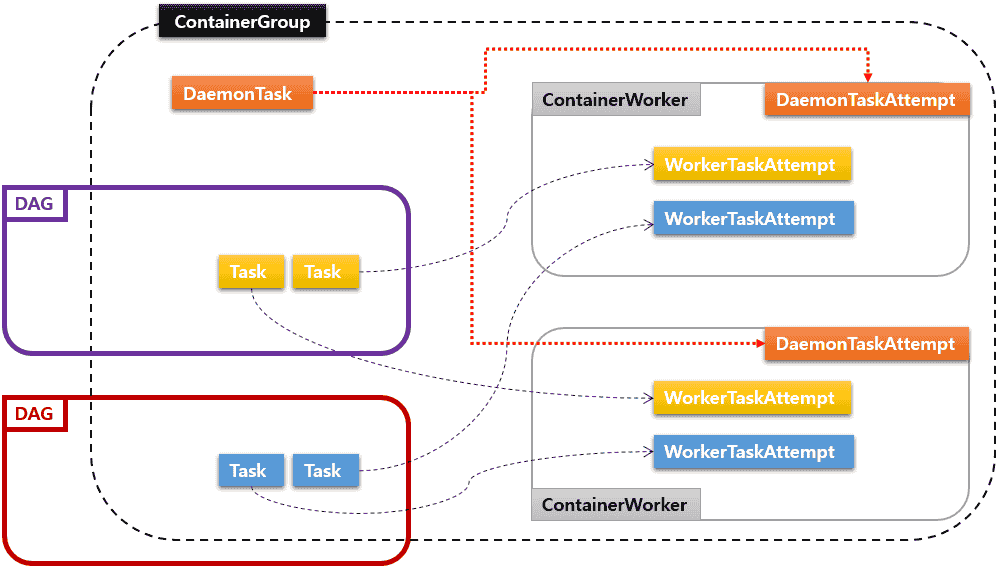
The state of a DaemonTask is shared by all ContainerWorkers in the same ContainerGroup. All events relevant to its service are always broadcast to all DaemonTaskAttempts, and in principle, a DaemonTaskAttempt created for a new ContainerWorker receives the entire history of such events upon its start. For example, the DaemonTask implementing the shuffle service in the ASM runtime maintains a table of addresses and ports of all its DaemonTaskAttempts and sends it to every new DaemonTaskAttempt. Thus, in order for all DaemonTaskAttempts to stay up-to-date with each other, it suffices to just handle events sent from the DaemonTask.
Since DaemonTasks are not a part of MR3 DAGs, DaemonTaskAttempts do not have input/output TaskAttempts and run independently of WorkerTaskAttempts. Note, however, that DaemonTaskAttempts can still perform I/O of their own such as network transmission and disk access. In fact, a typical usage of DaemonTaskAttempts is to perform I/O in the background while WorkerTaskAttempts produce or consume intermediate data.
A ContainerWorker starts DaemonTaskAttempts before accepting WorkerTaskAttempts. If any DaemonTaskAttempt fails to initialize, the ContainerWorker itself stops because subsequent WorkerTaskAttempts expect the service provided by DaemonTaskAttempts.